Set up Disaster Recovery (Site-to-site VPN)
You can set up disaster recovery using your Site-to-site VPN connection between two Yeastar P-Series Software Editions, so as to ensure the continuous availability of essential telephony services in the event of a disaster.
Requirements
Both servers in a disaster recovery pair must meet the following requirements.
| Item | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Product Model | Yeastar P-Series Software Edition |
| Plan | Ultimate Plan |
| Version | Same firmware version and must be 83.12.0.57 or later. |
| Network | LAN port as the default Ethernet interface and a static IP address is required. |
| External Storage | Identical storage device settings and mounting points. |
Prerequisites
You have connected two Yeastar P-Series Software Editions using Site-to-site VPN, and they can communicate with each other.
Procedure
To implement disaster recovery, you need to complete the following settings on both Working Server and Redundancy Server.
- Log in to PBX web portal, go to .
- Enable disaster recovery and set the remote networking method.
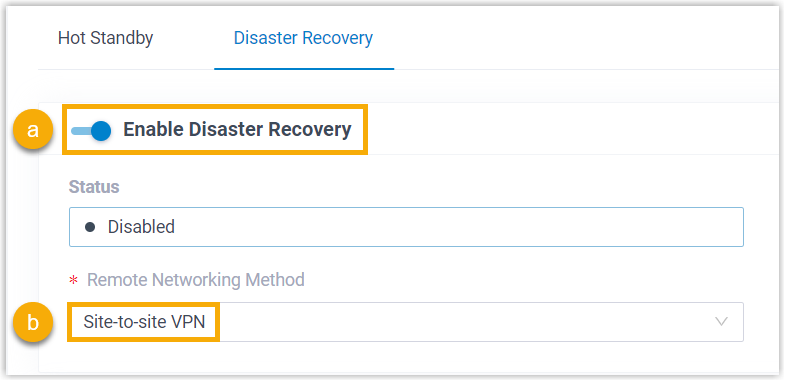
- On the top of the page, turn on the Enable Disaster Recovery switch.
- In the Remote Networking Method drop-down list, select Site-to-site VPN.
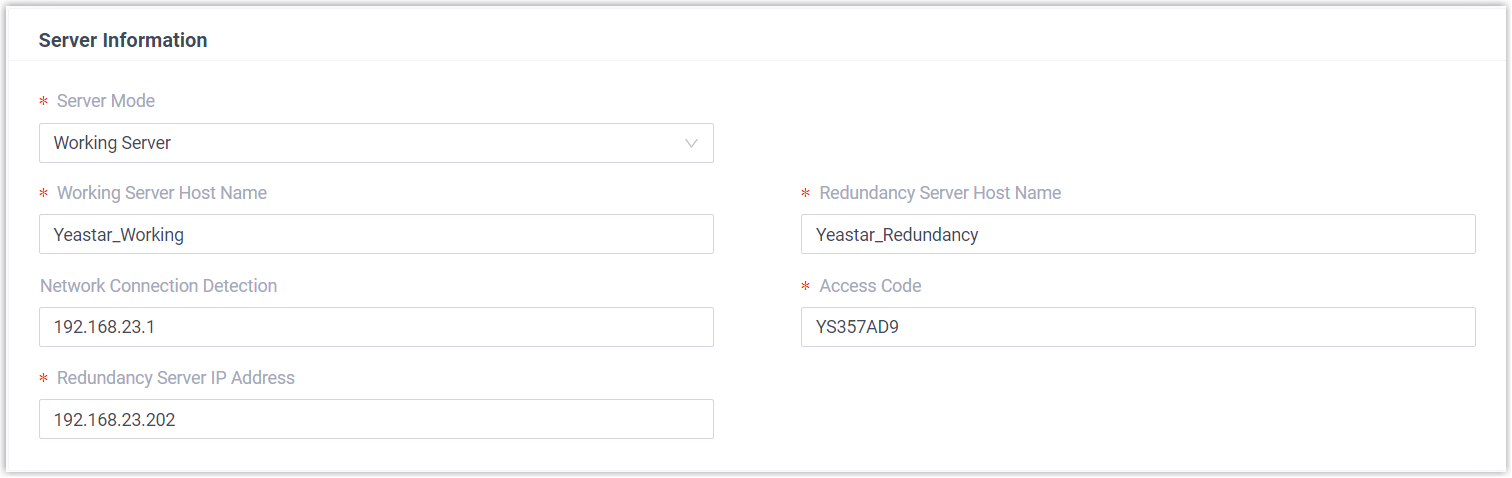
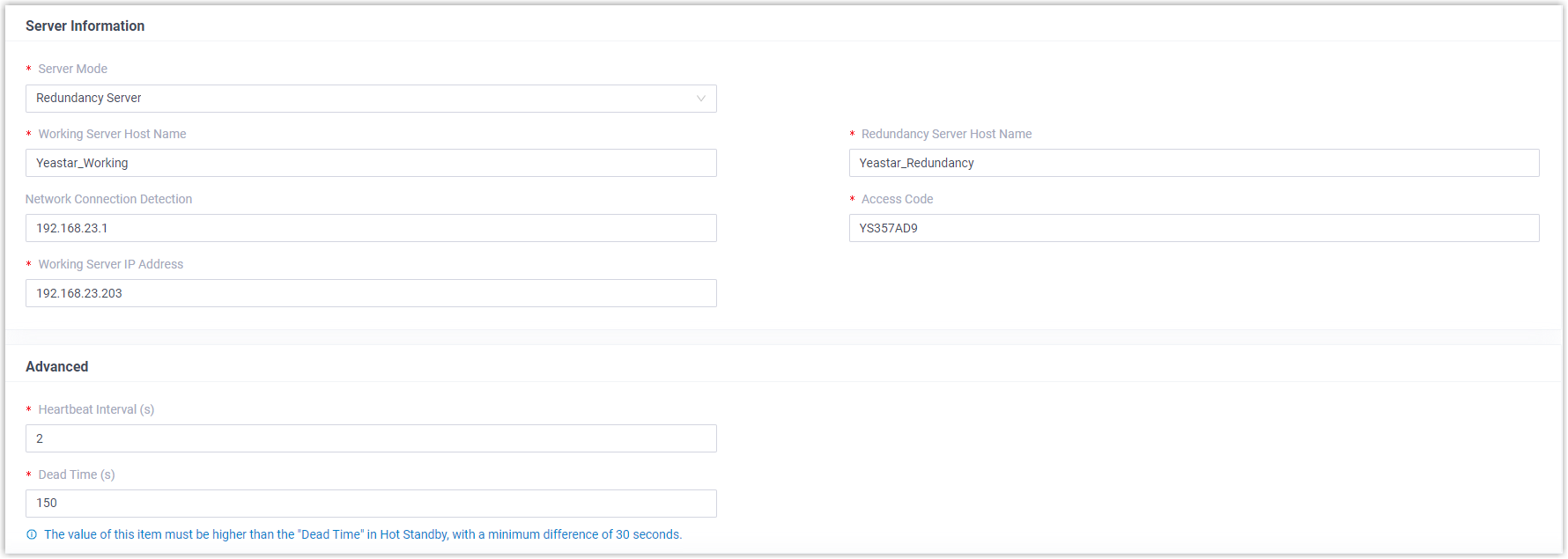
- Complete the following settings for the disaster recovery pair.
- Working Server
- Redundancy Server
- Click Save.
The system prompts that you need to reboot the PBXs to make disaster recovery take effect.
- Click Reboot Now.
Result
- On Working Server, the status is displayed as
Working, indicating that the server is running to
provide all PBX functions.
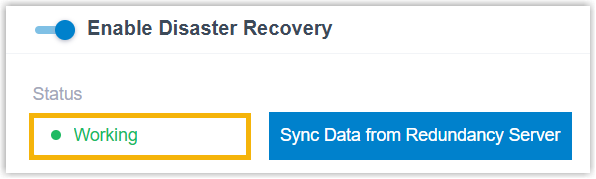 Note: The Sync Data from the Redundancy Server button that appears next to the Status field can be used to synchronize data (CDR and recordings) from the Redundancy Server, so as to eliminate the data differential after the Working Server takes over service, or when both servers ran independently due to a temporary network interruption.
Note: The Sync Data from the Redundancy Server button that appears next to the Status field can be used to synchronize data (CDR and recordings) from the Redundancy Server, so as to eliminate the data differential after the Working Server takes over service, or when both servers ran independently due to a temporary network interruption.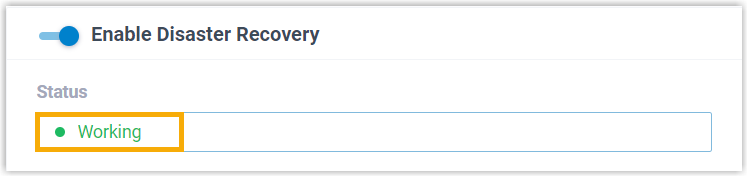
Upon successfully synchronized, the relevant contacts will receive a Working Server Manual Data Synchronization Completed event notification.
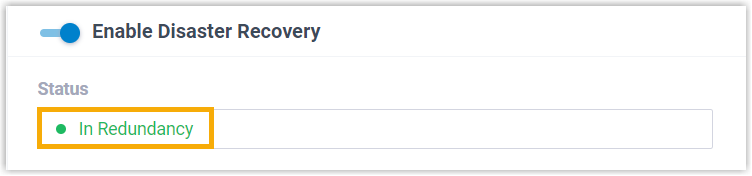
- On Redundancy Server, the status is displayed as In
Redundancy, indicating that the server is in redundancy
status. The Redundancy Server will now replicate data from the Working
Server.
What to do next
Read Server Redundancy on SIP Trunks and WebRTC Trunks and Server Redundancy on SIP Devices and Linkus UC Clients to learn how server redundancy can be implemented on trunks and extension endpoints.