IP Phone Configuration Guide Overview
Yeastar P-Series Software Edition supports most SIP-based IP phones, allowing you to configure IP phones to work with the PBX system. This topic describes different configuration methods (including phone provisioning and extension registration) to help you understand the configuration process between IP phones and Yeastar P-Series Software Edition, and offers the detailed configuration guides for the IP phones of many popular phone vendors.
Configuration methods
Yeastar supports multiple configuration methods to help you connect your IP phones to Yeastar PBX, as the following table shows.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Provision a large number of identical IP phones at one time
to complete general settings (preferences, codecs, etc) and
extension registration, which significantly improves deployment
efficiency. In addition, the IP phones can be managed centrally
on Yeastar P-Series Software Edition. This method is applicable for IP phones that support Auto Provisioning. |
|
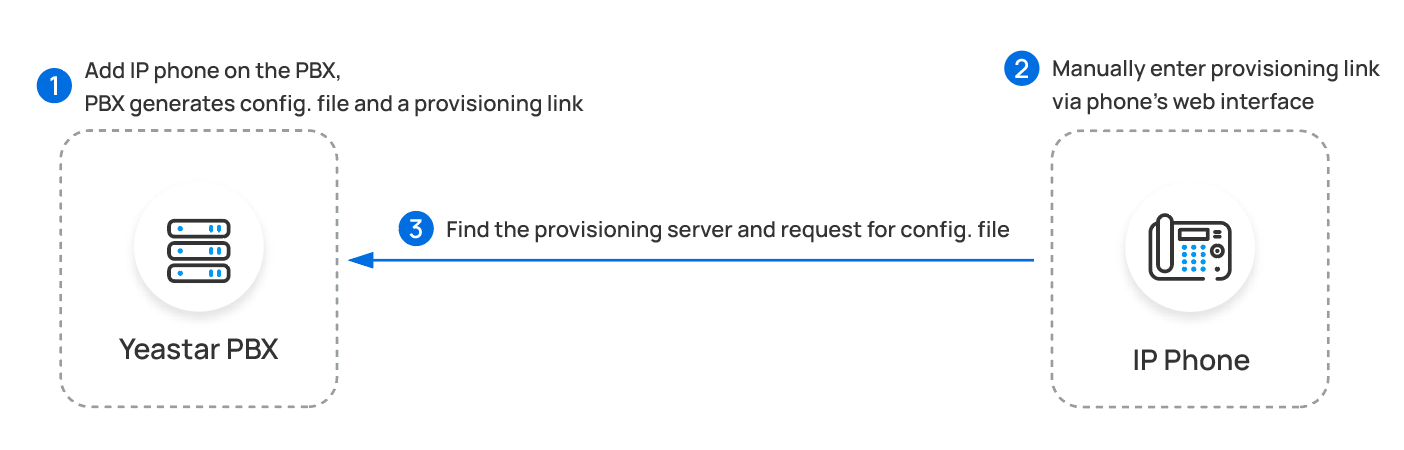
| Manual Provisioning | Provision IP phones one by one by manually entering a
PBX-provided provisioning link on the phone's web interface, so
as to complete general settings (preference, codecs, etc) and
extension registration. This method is mainly used for IP phones that do NOT support RPS auto provisioning. |
| Manual Registration | Register PBX extension(s) on an IP phone, without additional
phone auto provisioning. This method is applicable for IP phones that are compatible with the standard SIP protocol. |
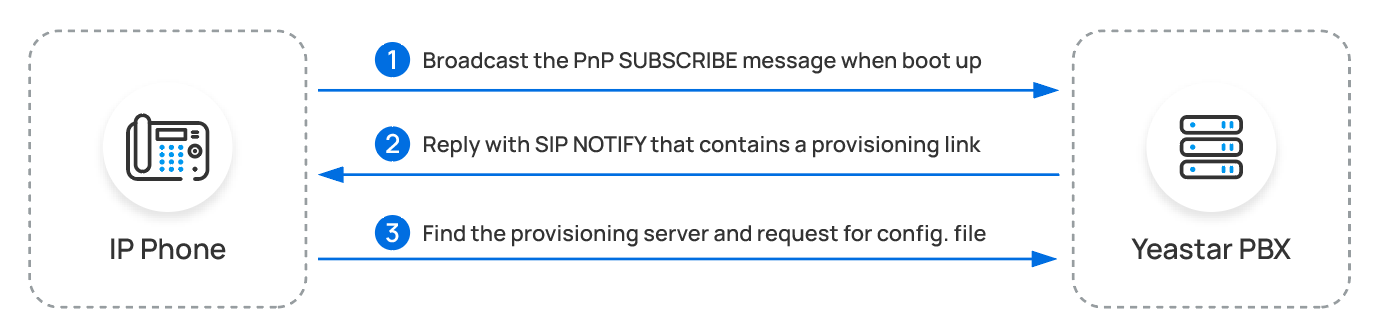
- PnP (Plug and Play) method
- If your IP phone is deployed in the SAME subnet as the PBX and supports PnP provisioning, you can auto provision the phone via PnP method.
- DHCP method
- According to the network environment of IP phone and Yeastar PBX,
you can auto provision IP phones using the PBX's built-in DHCP
server or a third-party DHCP server:
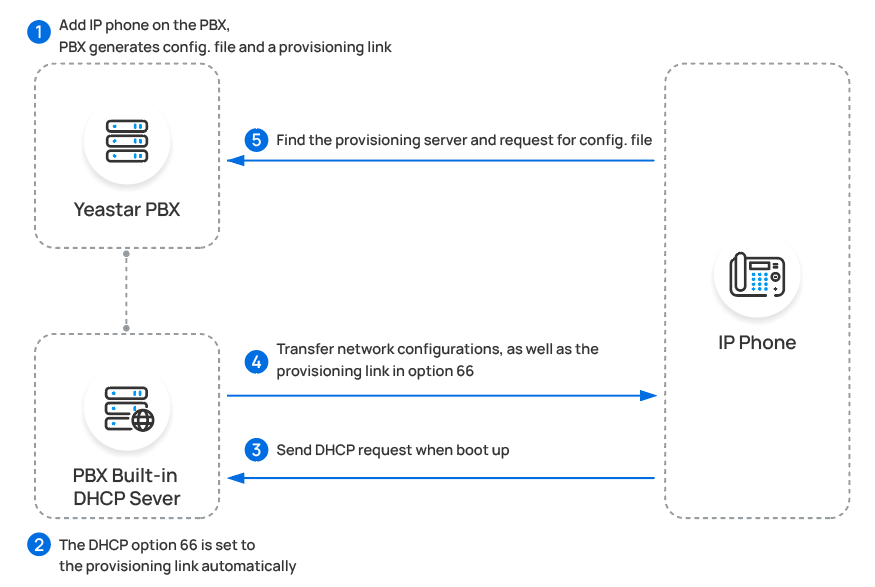
Scenario Description IP phone is deployed in the SAME subnet as the PBX, but does NOT support PnP provisioning In this scenario, you can use the PBX's built-in DHCP server. The provisioning process is shown below:
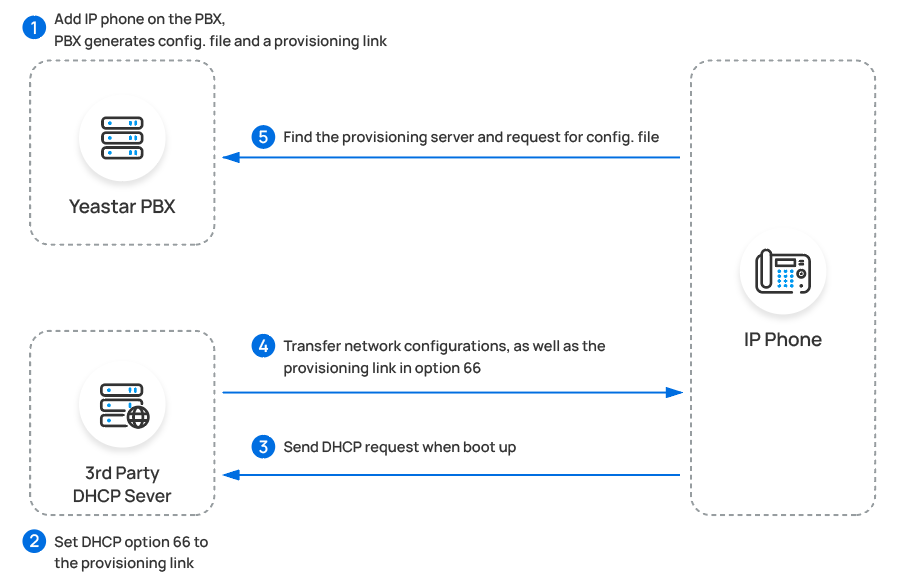
IP phone and PBX are deployed in DIFFERENT subnets In this scenario, you can use a third-party DHCP server. The provisioning process is shown below:
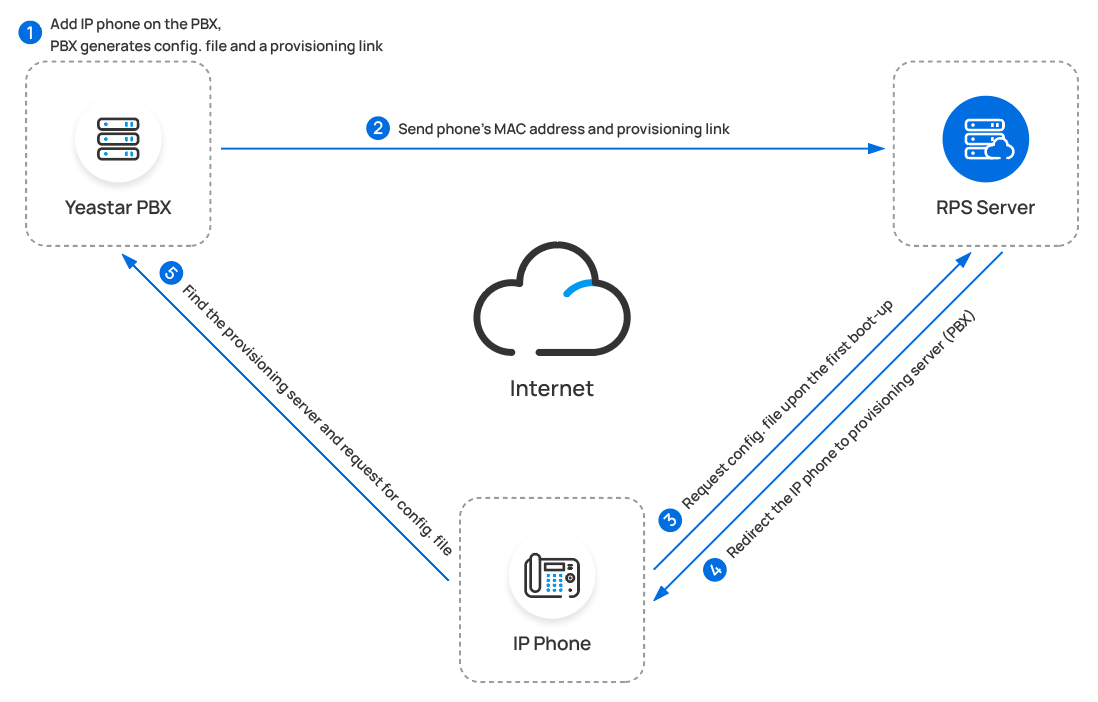
- RPS (Redirection and Provisioning Service) method
- If your IP phone is deployed in remote network, you can provision the phone via RPS method, either using public IP address or Yeastar FQDN of the PBX.
You can manually register IP phones to Yeastar PBX by entering the SIP credentials (extension information and PBX server information) on the phone's web interface.
The registration process is shown below:

Configuration guides
Based on the configuration methods mentioned above, the following configuration guides offer detailed instructions to assist you in configuring IP phones from various phone vendors.