Auto Provision Yealink IP Phone with Yeastar P-Series Software Edition
This topic takes Yealink SIP-T53W (firmware: 96.85.0.5) as an example to introduce how to auto provision a Yealink IP phone with Yeastar P-Series Software Edition.
Requirements
The firmwares of Yealink IP Phone and Yeastar PBX meet the following requirements.
| Model | Phone Requirement | PBX Requirement | Supported Auto Provisioning Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| AX83H | 180.86.0.5 or later |
83.16.0.25 or later |
|
| AX86R | 180.86.0.5 or later |
83.18.0.59 or later |
|
| CP920 | 78.85.0.5 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| CP925 | 148.86.0.5 or later |
83.5.0.9 or later |
|
| CP960 | 73.85.0.5 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| CP965 | 143.86.0.5 or later |
83.5.0.9 or later |
|
| SIP-CP935W | 149.86.0.5 or later |
83.5.0.9 or later |
|
| SIP-T19P_E2 | 53.84.0.125 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T20P | 9.73.0.50 or later |
83.20.0.74 or later |
|
| SIP-T21_E2 | 52.84.0.125 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T21P_E2 | 52.84.0.125 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T22P | 7.73.0.50 or later |
83.20.0.74 or later |
|
| SIP-T23G | 44.84.0.125 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T23P | 44.84.0.125 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T26P | 6.73.0.50 or later |
83.20.0.74 or later |
|
| SIP-T27G | 69.85.0.5 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T28P | 2.73.0.50 or later |
83.20.0.74 or later |
|
| SIP-T29G | 46.83.0.120 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T30 | 124.85.0.15 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T30P | 124.85.0.15 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T31 | 124.85.0.15 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T31G | 124.85.0.15 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T31P | 124.85.0.15 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T31W | 124.86.0.75 or later |
83.11.0.56 or later |
|
| SIP-T32G | 32.70.0.125 or later |
83.20.0.74 or later |
|
| SIP-T33G | 124.85.0.15 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T33P | 124.85.0.15 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T34W | 124.86.0.75 or later |
83.12.0.23 or later |
|
| SIP-T38G | 38.70.0.185 or later |
83.20.0.74 or later |
|
| SIP-T40G | 76.84.0.125 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T40P | 54.84.0.125 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T41P | 36.83.0.120 or later |
83.20.0.74 or later |
|
| SIP-T41S | 66.85.0.5 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T41U | 108.85.0.39 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T42G | 29.83.0.120 or later |
83.20.0.74 or later |
|
| SIP-T42S | 66.85.0.5 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T42U | 108.85.0.39 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T43U | 108.85.0.39 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T44U | 108.86.0.90 or later |
83.10.0.32 or later |
|
| SIP-T44W | 108.86.0.90 or later |
83.10.0.32 or later |
|
| SIP-T46G | 28.83.0.120 or later |
83.20.0.74 or later |
|
| SIP-T46S | 66.85.0.5 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T46U | 108.85.0.39 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T48G | 35.83.0.120 or later |
83.20.0.74 or later |
|
| SIP-T48S | 66.85.0.5 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T48U | 108.85.0.39 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T52S | 70.84.0.70 or later |
83.20.0.74 or later |
|
| SIP-T53 | 96.85.0.5 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T53W | 96.85.0.5 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T54S | 70.84.0.70 or later |
83.20.0.74 or later |
|
| SIP-T54W | 96.85.0.5 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T56A | 58.83.0.15 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T57W | 96.85.0.5 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T58 | 58.85.0.5 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T58W | 150.86.0.5 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| SIP-T73W | 185.87.0.15 or later |
83.19.0.70 or later |
|
| SIP-T73U | 185.87.0.15 or later |
83.19.0.70 or later |
|
| SIP-T74LTE | 185.87.0.33 or later |
83.19.0.70 or later |
|
| SIP-T74LTE(US) | 185.87.0.33 or later |
83.19.0.70 or later |
|
| SIP-T74W | 185.87.0.15 or later |
83.19.0.70 or later |
|
| SIP-T74U | 185.87.0.15 or later |
83.19.0.70 or later |
|
| SIP-T77U | 185.87.0.15 or later |
83.19.0.70 or later |
|
| SIP-T85W | 185.87.0.15 or later |
83.19.0.70 or later |
|
| SIP-T87W | 185.87.0.15 or later |
83.19.0.70 or later |
|
| SIP-T88W | 192.87.0.5 or later |
83.19.0.70 or later |
|
| SIP-T88V | 192.87.0.5 or later |
83.19.0.70 or later |
|
| T64LTE | 132.86.0.25 or later |
83.16.0.71 or later |
|
| T67LTE | 132.86.0.35 or later |
83.16.0.71 or later |
|
| VP59 | 91.85.0.5 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| W60B (W53P, W41P, W60P, CP930W-Base) | 77.83.0.85 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| W70B (W79P, W76P, W73P) | 146.85.0.20 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| W75DM | 175.85.0.5 or later | 83.14.0.26 or later |
|
| W80B | W80DM-103.83.0.80 |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
| W90DM | 130.85.0.15 or later |
83.4.0.17 or later |
|
Scenarios
The provisioning methods and operations vary depending on the network environment of Yealink IP Phone and Yeastar PBX, as the following table shows.
| Scenario | Description |
|---|---|
| IP Phone and PBX are in the SAME subnet (LAN) | In this scenario, you can provision the Yealink IP phone with
the PBX via PnP method. For more information, see Auto provision a Yealink IP phone in the same subnet (PnP). |
| IP Phone and PBX are in DIFFERENT subnets (LAN) | In this scenario, you can provision the Yealink IP phone with
the PBX via DHCP method. For more information, see Auto provision a Yealink IP phone in the different subnets (DHCP). |
| IP Phone and PBX are in DIFFERENT network | In this scenario, you can provision the Yealink IP phone with
the PBX via RPS method. For more information, see Auto provision a Yealink IP phone in remote network (RPS). |
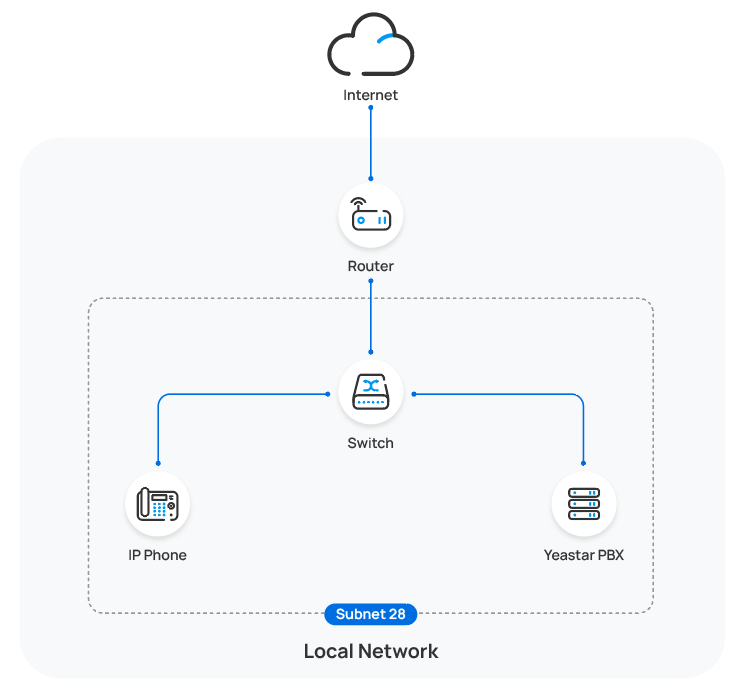
Auto provision a Yealink IP phone in the same subnet (PnP)
In this example, the Yealink IP phone (IP: 192.168.28.192) and the
Yeastar PBX (IP: 192.168.28.39) are both deployed in subnet 28.
- Prerequisites
-
- Make sure that you have downloaded the template for the desired phone model (Path: ).
- If the IP phone is previously used, you need to RESET the IP phone, then re-configure the network settings for the phone.
- Procedure
-
- Log in to PBX web portal, go to .
The IP phones detected by the PBX via PnP are displayed in the phone list.
- Click
 beside the Yealink IP
phone.
beside the Yealink IP
phone.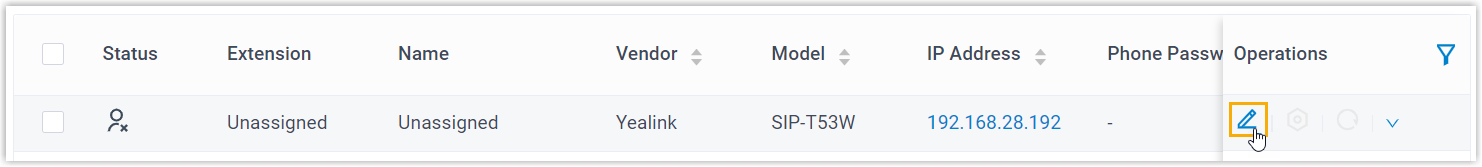
- Optional: In the Options section,
select a desired template from the Template
drop-down list.Note: You can select the default template corresponding to the phone model, or customize your own template. For more information, see Create a Custom Auto Provisioning Template.
- In the Assign Extension
section, assign an extension to the IP phone.
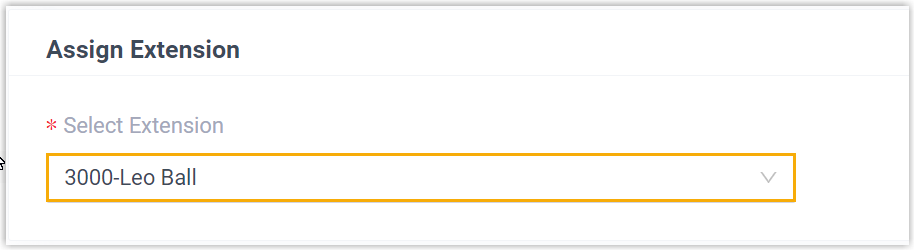 Note: If your desired extension is not listed in the drop-down list, it indicates that the extension has been associated with an IP phone or gateway.
Note: If your desired extension is not listed in the drop-down list, it indicates that the extension has been associated with an IP phone or gateway.- To release the extension from the associated IP phone or gateway, see Release an Extension from a Provisioned IP Phone/Gateway.
- To assign the extension to the phone without releasing it from the previously associated device, you can configure the concurrent registration setting for the extension, as the PBX only allows an extension to register with one SIP endpoint by default.
- Click Save.
- Set a password for Admin account.Note: If automatic random password generation for phones is enabled, this step can be skipped.
- Click
 beside the IP
phone.
beside the IP
phone. - In the Preference section, set a
password in the Admin Phone
Password field.
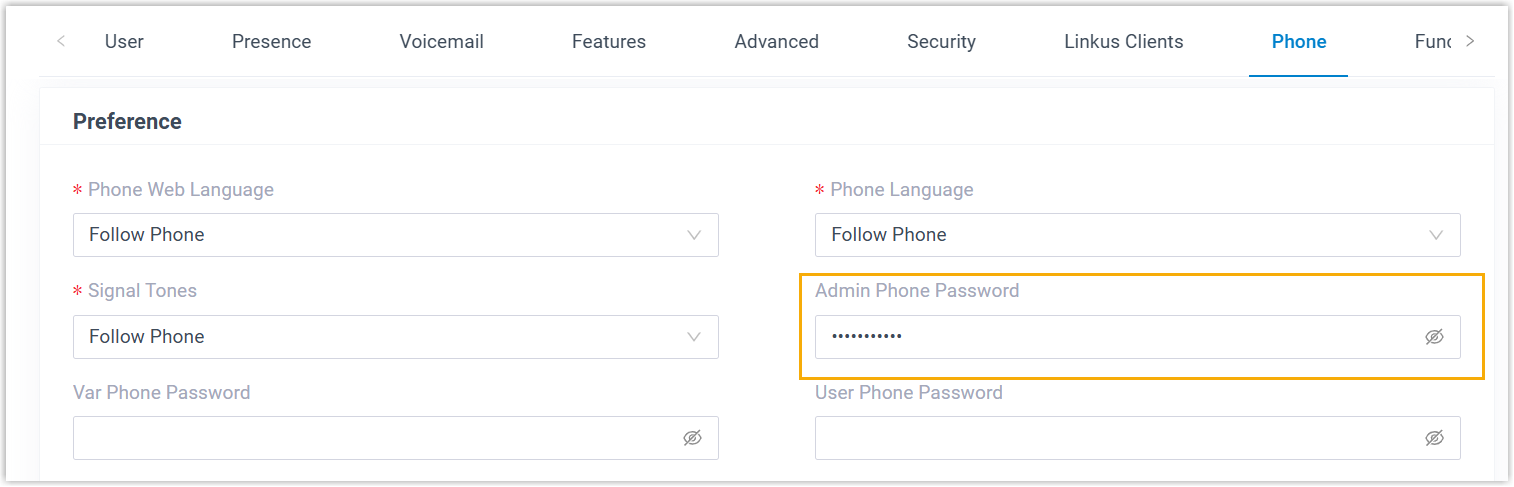
- Click Save.
- Click
- Log in to PBX web portal, go to .
- Result
-
Note: Some IP phones will reboot automatically. If not, you need to manually reboot the phone to make the configurations take effect.
- The IP phone automatically downloads the configurations from the PBX and applies the settings.
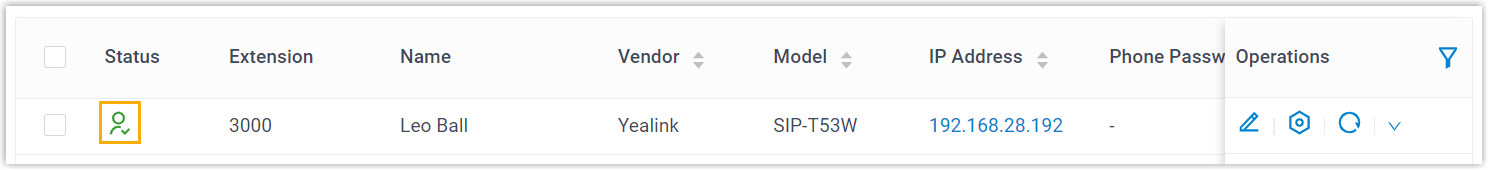
- The extension is successfully registered on the IP phone. You
can check the registration status on in PBX web portal.
Auto provision a Yealink IP phone in the different subnets (DHCP)
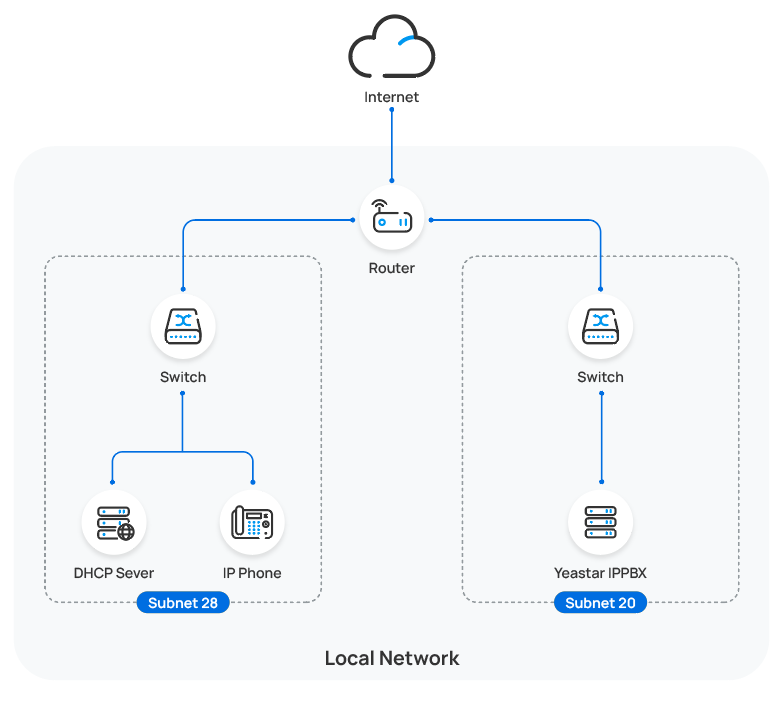
In this example, the Yealink IP phone and a DHCP server are deployed in subnet 28,
while the Yeastar PBX (IP: 192.168.20.58) is deployed in subnet
20.
- Prerequisites
-
- Make sure that there is only one DHCP server running in the subnet where the IP phone is deployed, or the IP phone would fail to obtain an IP address.
- Make sure that the IP phone and PBX can communicate with each other over the subnets.
- Make sure that you have downloaded the template for the desired phone model (Path: ).
- RESET the IP phone if it is previously used.
- Gather information of IP phone, including Vendor, Model, and MAC address.
- Procedure
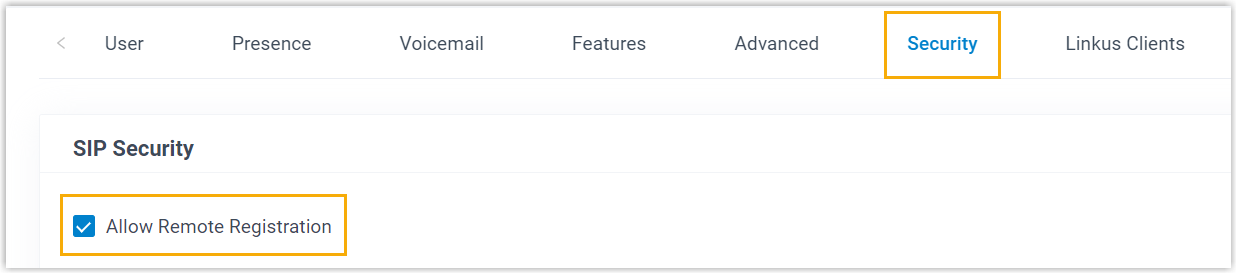
- Step 1. Enable Remote Registration feature for the extension on PBX
- Enable the Remote Registration feature for the extension to be assigned to the phone, so that the extension can be registered in a different subnet.
- Step 2. Add the Yealink IP phone on PBX
-
- On PBX web portal, go to .
- Click .
- In the IP Phone section, enter the
following phone information.
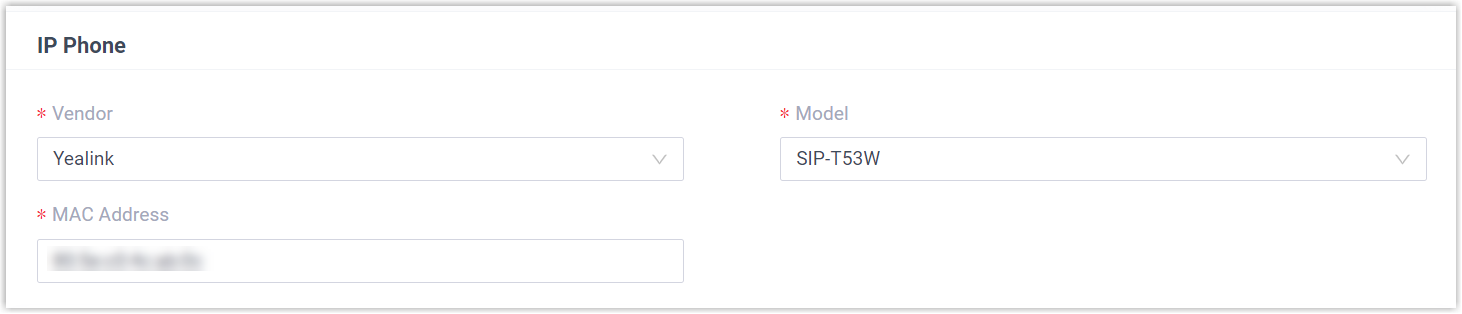
- Vendor: Select Yealink.
- Model: Select the phone model. In this example, select SIP-T53W.
- MAC Address: Enter the MAC address of the IP phone.
- In the Options section,
configure the following settings.
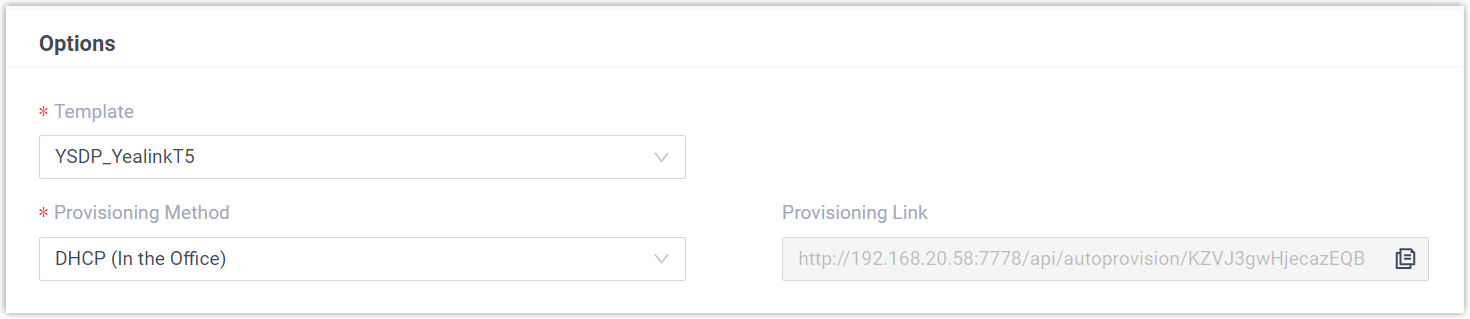
- Template: Select a desired template
from the drop-down list.Note: You can select the default template corresponding to the phone model, or customize your own template. For more information, see Create a Custom Auto Provisioning Template.
- Provisioning Method: Select
DHCP (In the Office).
A provisioning link is automatically generated and displayed in the Provisioning Link field. This provisioning link points to the location where the phone's configuration file is stored.
- Template: Select a desired template
from the drop-down list.
- In the Assign Extension
section, assign an extension to the IP phone.
 Note: If your desired extension is not listed in the drop-down list, it indicates that the extension has been associated with an IP phone or gateway.
Note: If your desired extension is not listed in the drop-down list, it indicates that the extension has been associated with an IP phone or gateway.- To release the extension from the associated IP phone or gateway, see Release an Extension from a Provisioned IP Phone/Gateway.
- To assign the extension to the phone without releasing it from the previously associated device, you can configure the concurrent registration setting for the extension, as the PBX only allows an extension to register with one SIP endpoint by default.
- Click Save.
- Set a password for Admin account.Note: If automatic random password generation for phones is enabled, this step can be skipped.
- Click
 beside the IP
phone.
beside the IP
phone. - In the Preference section, set a
password in the Admin Phone
Password field.

- Click Save.
- Click
- Step 3. Configure DHCP option 66 on DHCP server
-
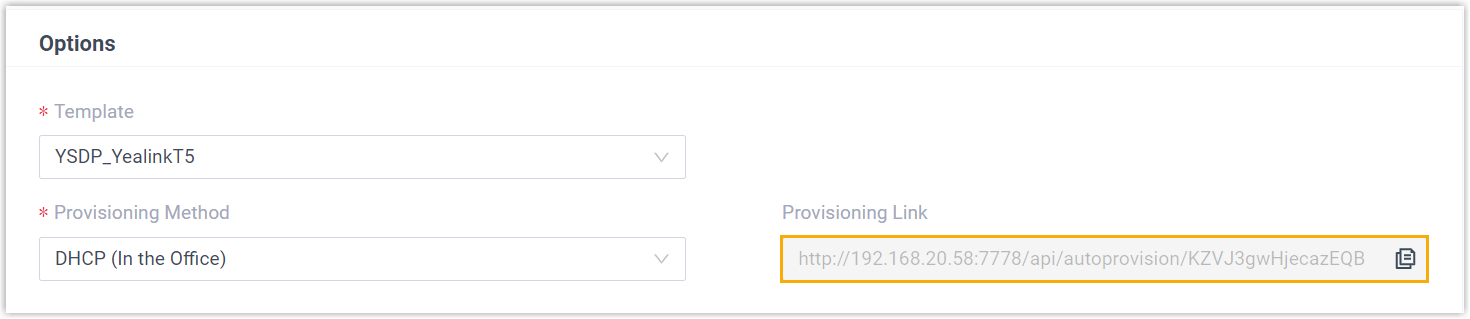
In the subnet where the IP phone is deployed, use the generated provisioning link to configure option 66 on the DHCP Server.
- On PBX web portal, copy the provisioning link from the phone's
detail page.
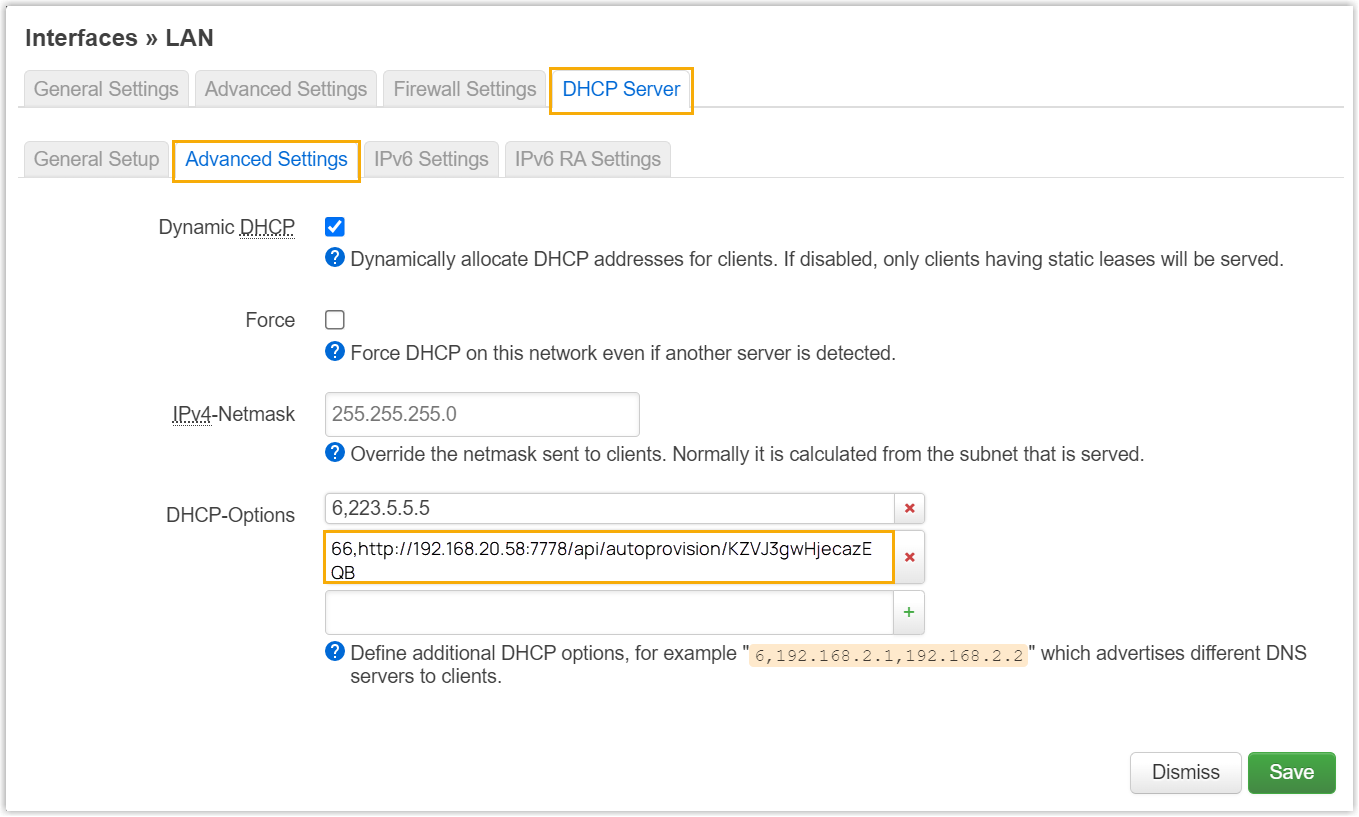
- On the DHCP server, set up option 66 with the
provisioning link.
In this example, the configuration on a router's DHCP server is shown below.
- On PBX web portal, copy the provisioning link from the phone's
detail page.
- Result
-
Note: Some IP phones will reboot automatically. If not, you need to manually reboot the phone to make the configurations take effect.
- After the IP phone is rebooted, it gets an IP address from the DHCP server, downloads the configurations from the PBX via the provisioning link, and applies the settings automatically.
- The extension is successfully registered on the IP
phone. You can check the registration status on on the PBX web portal.
Auto provision a Yealink IP phone in remote network (RPS)
In this example, the Yealink IP phone and the Yeastar PBX are deployed in different network.
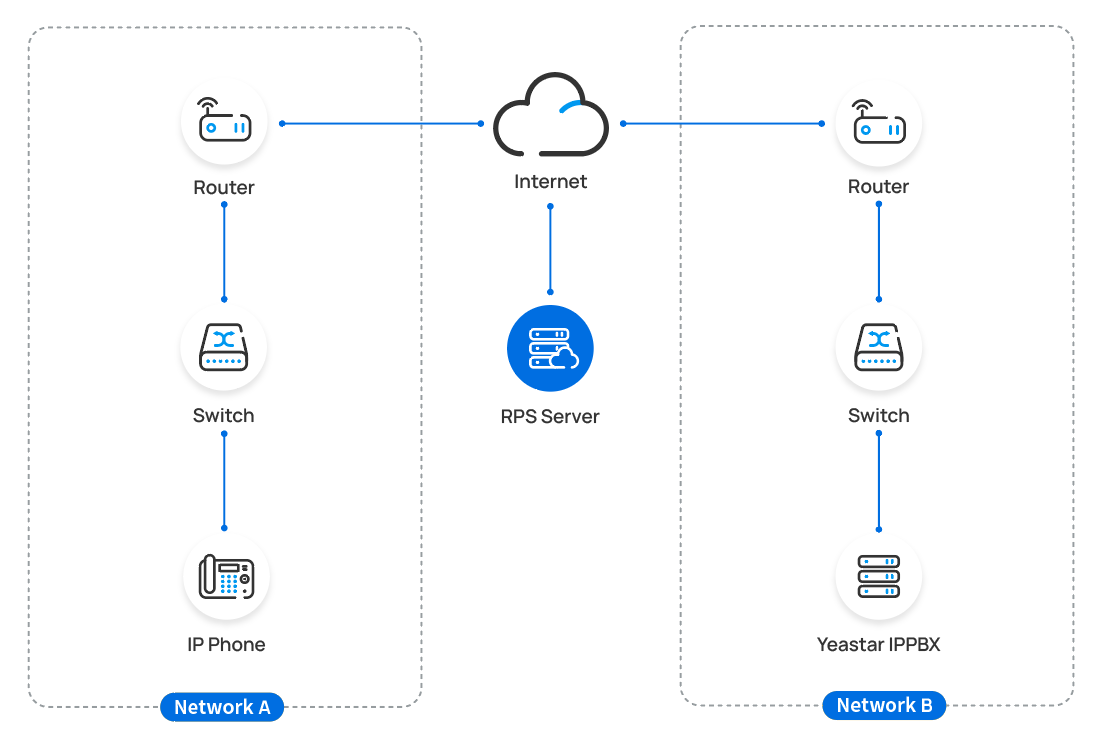
- Prerequisites
- Yeastar P-Series Software Edition supports to auto provision a Yealink phone remotely either using Yeastar FQDN or using Public IP address / domain name. According to the provisioning method you intend to use, make sure that you have completed the corresponding setup shown below.
- Procedure
- Step 1. Add the Yealink IP phone on PBX
-
- Log in to PBX web portal, go to .
- Click .
- In the IP Phone section, enter the
following phone information.

- Vendor: Select Yealink.
- Model: Select the phone model. In this example, select SIP-T53W.
- MAC Address: Enter the MAC address of the IP phone.
- In the Options section, configure the
following settings.
Figure 1. RPS using Yeastar FQDN 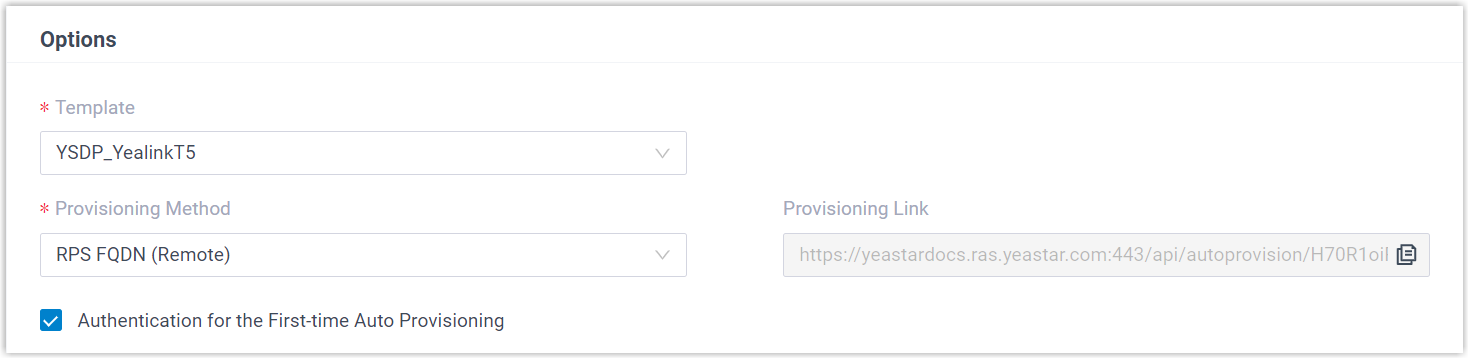
Figure 2. RPS using Public IP Address / External Host domain name / Yeastar Domain 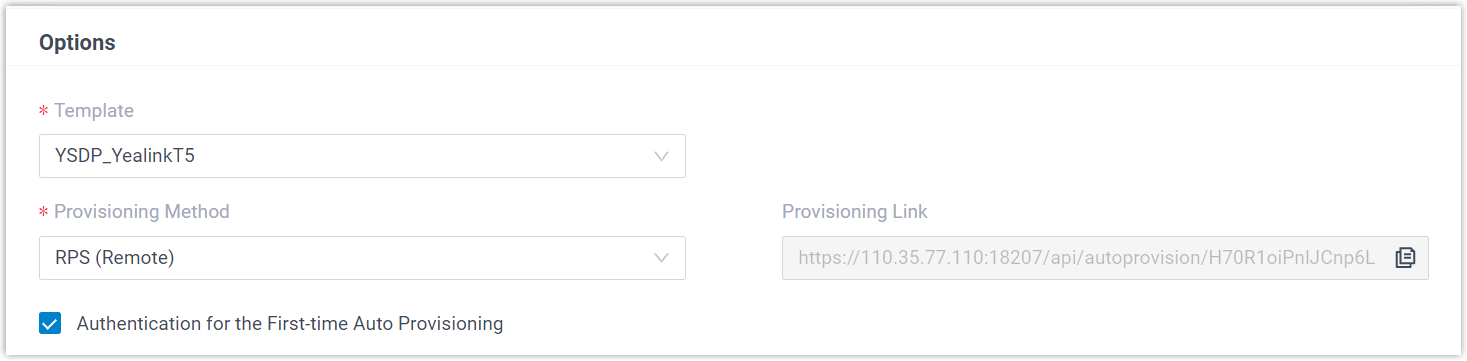
- Template: Select a
desired template from the drop-down list.Note: You can select the default template corresponding to the phone model, or customize your own template. For more information, see Create a Custom Auto Provisioning Template.
- Provisioning Method:
Select RPS FQDN (Remote) or
RPS (Remote) according to your
need.
A provisioning link is automatically generated and displayed in the Provisioning Link field. This provisioning link points to the location where the phone's configuration file is stored.
- Authentication for the
First-time Auto Provisioning: If enabled,
users are requested to fill in authentication information on
the IP phones before triggering the first-time
provisioning.Note: We recommend that you keep this option selected.
- Template: Select a
desired template from the drop-down list.
- In the Assign Extension
section, assign an extension to the IP phone.
 Note: If your desired extension is not listed in the drop-down list, it indicates that the extension has been associated with an IP phone or gateway.
Note: If your desired extension is not listed in the drop-down list, it indicates that the extension has been associated with an IP phone or gateway.- To release the extension from the associated IP phone or gateway, see Release an Extension from a Provisioned IP Phone/Gateway.
- To assign the extension to the phone without releasing it from the previously associated device, you can configure the concurrent registration setting for the extension, as the PBX only allows an extension to register with one SIP endpoint by default.
- Click Save.
The PBX will send an event notification of RPS Request Success.
- Set a password for Admin account.Note: If automatic random password generation for phones is enabled, this step can be skipped.
- Click
 beside the IP
phone.
beside the IP
phone. - In the Preference section, set a
password in the Admin Phone
Password field.

- Click Save.
- Click
- Step 2. Trigger the IP phone to complete provisioning
-
- Reboot the IP phone.
- If you have enabled Authentication for the First-time
Auto Provisioning on the PBX, enter the
authentication credential on the IP phone.
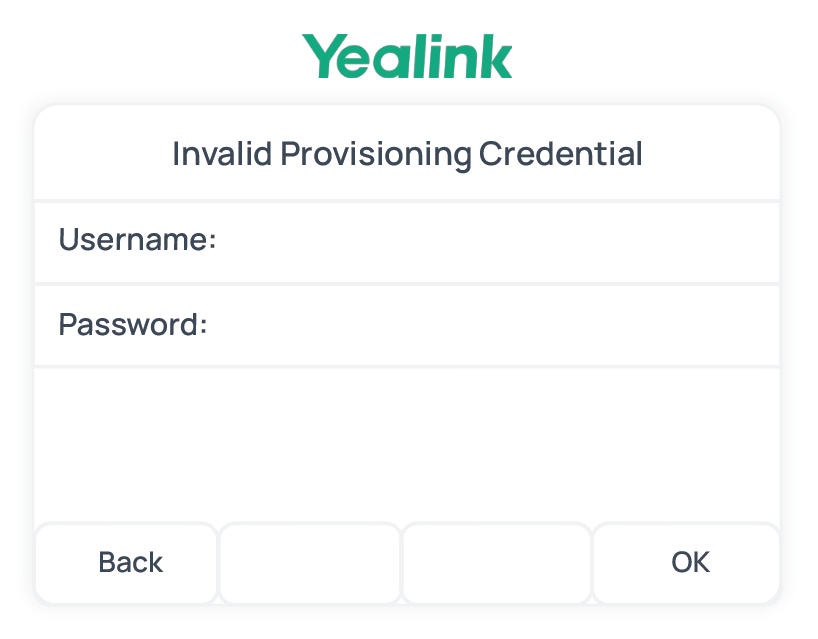
- Username: Enter the extension number that is assigned to the phone.
- Password: Enter the
extension's Voicemail Access PIN.Tip: You can check the Voicemail Access PIN in the Voicemail tab on the extension's configuration page.
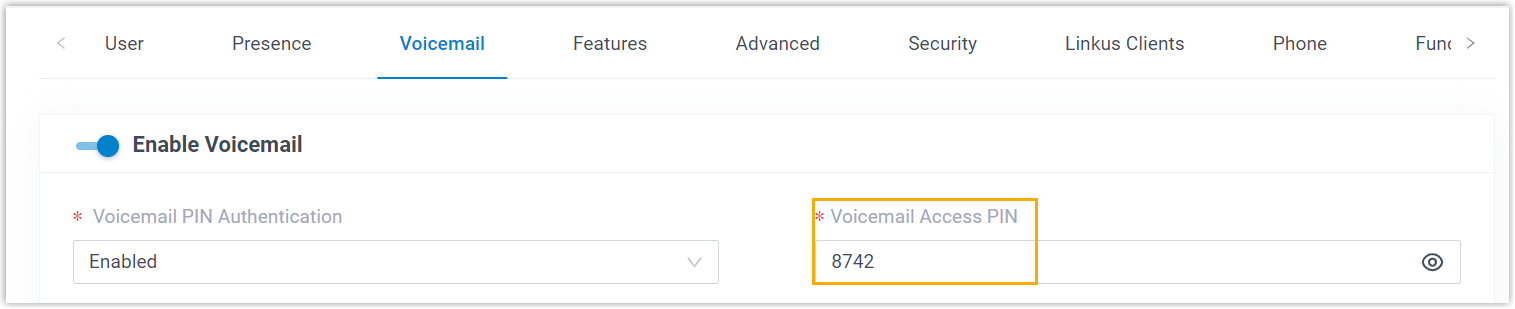
- Result
-
- The IP phone automatically downloads the configurations from the PBX and applies the settings.
- The extension is successfully registered on the IP
phone. You can check the registration status on on the PBX web portal.