Auto Provisioning Overview
Auto Provisioning is a time-saving feature that helps you to manage and deploy IP phones and gateways centrally on Yeastar P-Series PBX System. The process of configuring and managing IP phones and gateways is simplified, which makes deployment and management of devices fast and convenient.
Auto Provisioning supported devices
Yeastar P-Series PBX System supports various models for Auto Provisioning.
Find the Auto Provisioning - Supported Devices before you start deploying devices.
Auto Provisioning methods
Yeastar P-Series PBX System supports four Auto Provisioning methods, you can select a method to provision your IP phones and gateways according to your network environment.
- PnP (Plug and Play)
- PnP method supports auto provisioning IP phones and gateways that are
located in the same LAN subnet as the PBX.
For more information, see Auto Provision IP Phones in Local Network (PnP Method) and Auto Provision Yeastar TA FXS Gateways (PnP Method).
- DHCP Option 66
- DHCP method supports auto provisioning IP phones and gateways that are
located in the same local network as the PBX (same LAN subnet or different
LAN subnet).
For more information, see Auto Provision IP Phones in Local Network (DHCP Method) and Auto Provision Yeastar TA FXS Gateways (DHCP Method).
- RPS
- RPS method supports auto provisioning remote IP phones via public IP address or Yeastar FQDN.
- Provision Link
- Provision Link method supports auto provisioning remote IP phones/gateways
that don't support RPS Auto Provisioning method via public IP address or
Yeastar FQDN.Note: Cisco IP phones do not support Provision Link Auto Provisioning method.
How Auto Provisioning works
This section introduces how the Auto Provisioning methods work with IP phones and the PBX, which can help you understand the operating principle and locate the Auto Provisioning problem rapidly.
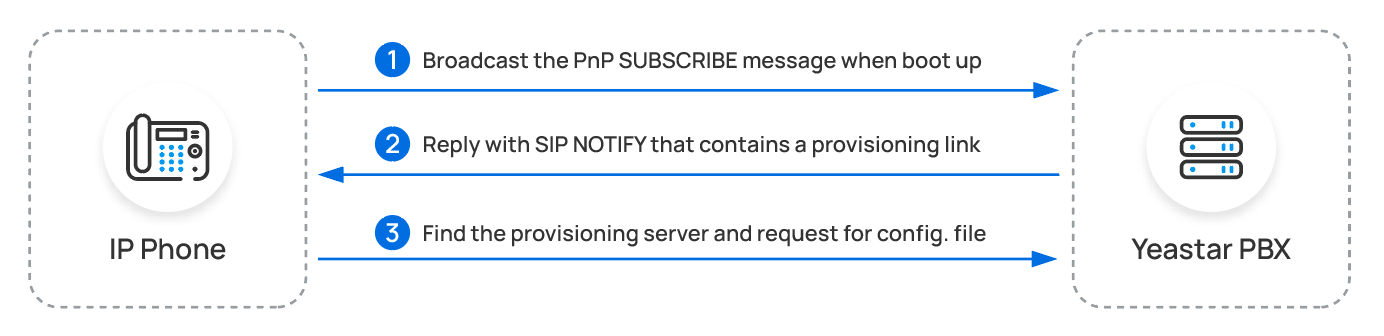
- PnP Provisioning
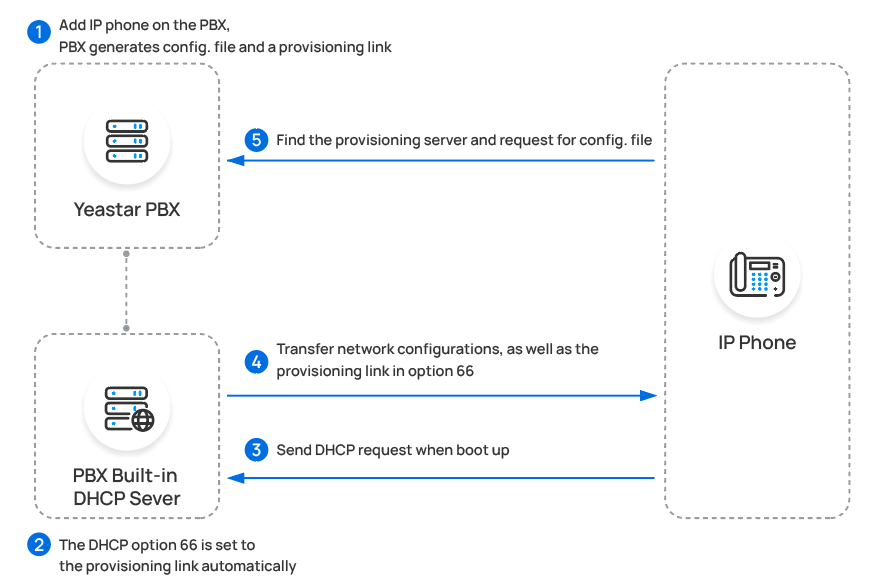
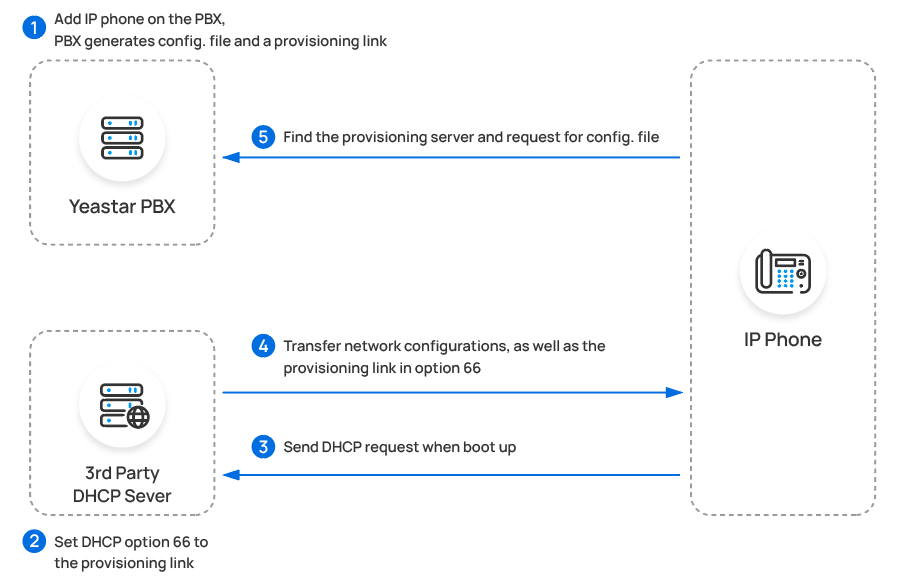
- DHCP Provisioning
-
You can directly use the PBX as a DHCP server, or use a third-party DHCP server that supports DHCP option 66.
Note: The DHCP server in the PBX supports only one DHCP address pool. - RPS Provisioning
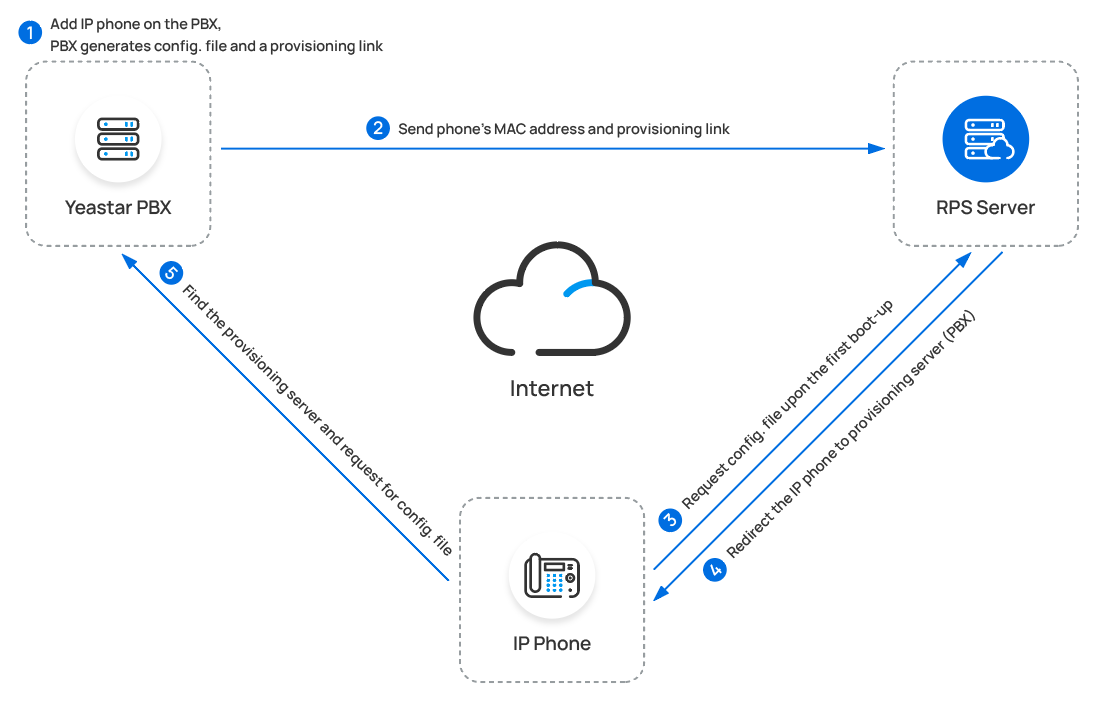
- Provision Link