Condition
This topic provides an overview of the Condition component, and describes its configuration as well as supported connections.
Component introduction
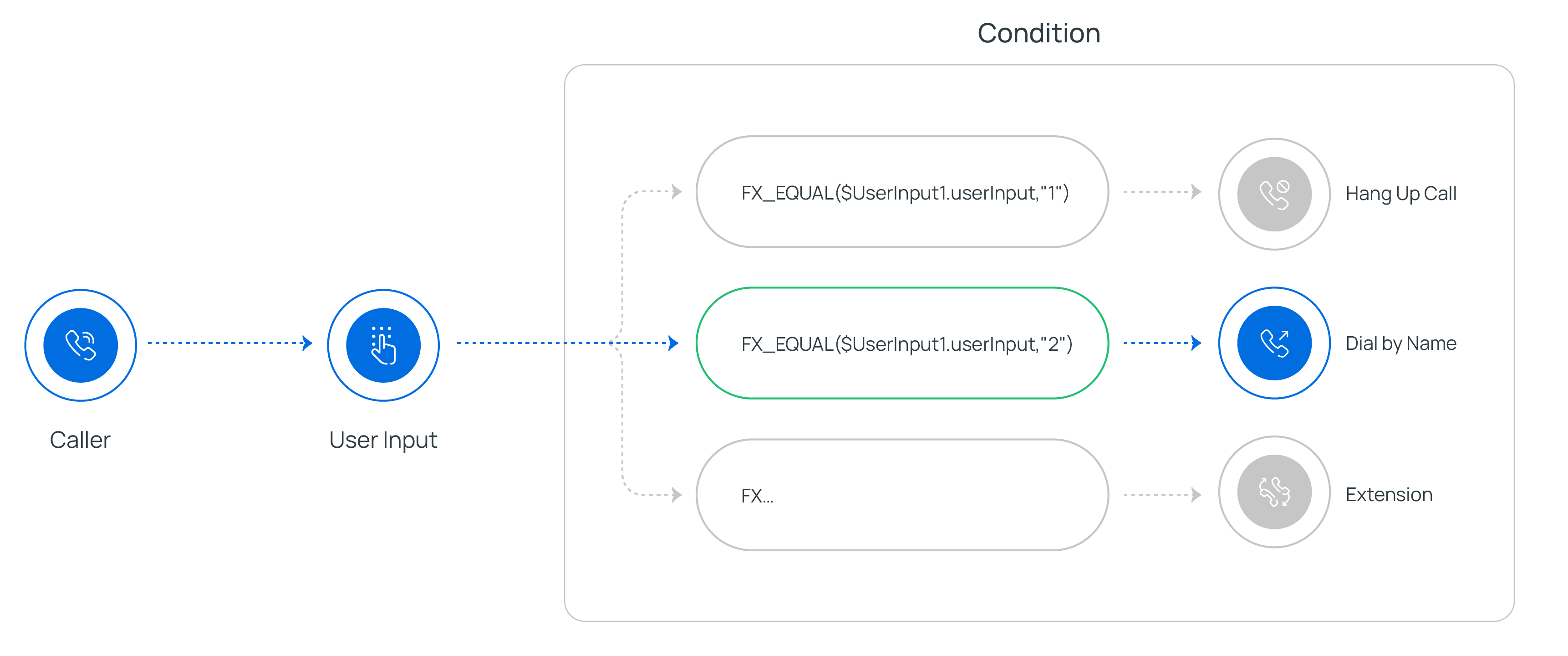
Condition component allows routing calls based on logical expressions. You can use variables, constants, and functions in an expression to evaluate specific conditions. When a condition is met, the call will be routed to the connected component.
Component configuration
After adding Condition component to a call flow, you can configure branches with expressions to route calls based on specific conditions.- Add branch(es) for different conditions
-
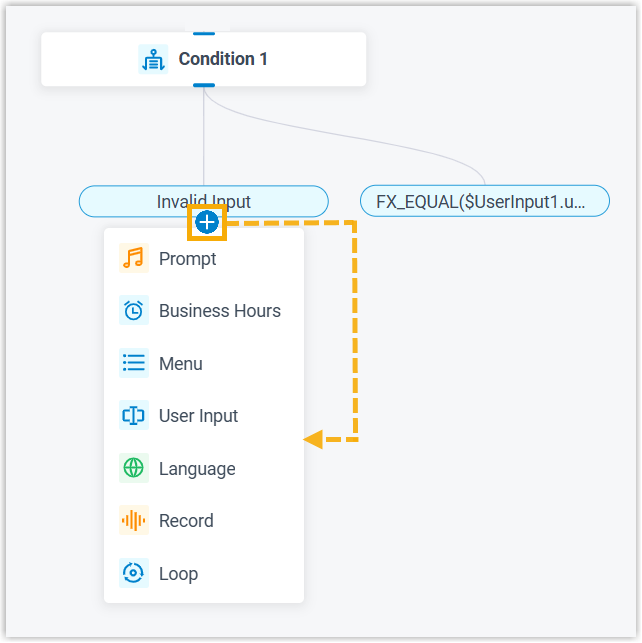
- Click
 on the component to add a branch.Note: You can add up to 10 branches, each associated with a unique expression.
on the component to add a branch.Note: You can add up to 10 branches, each associated with a unique expression.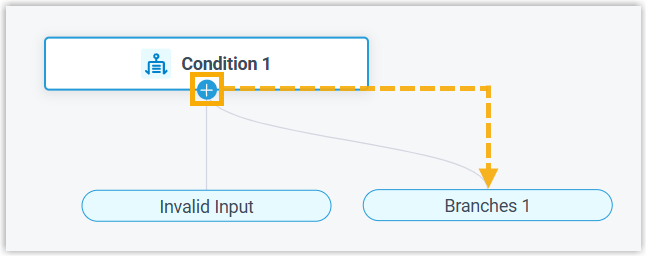
- Click the branch to configure expression, then click
Confirm.
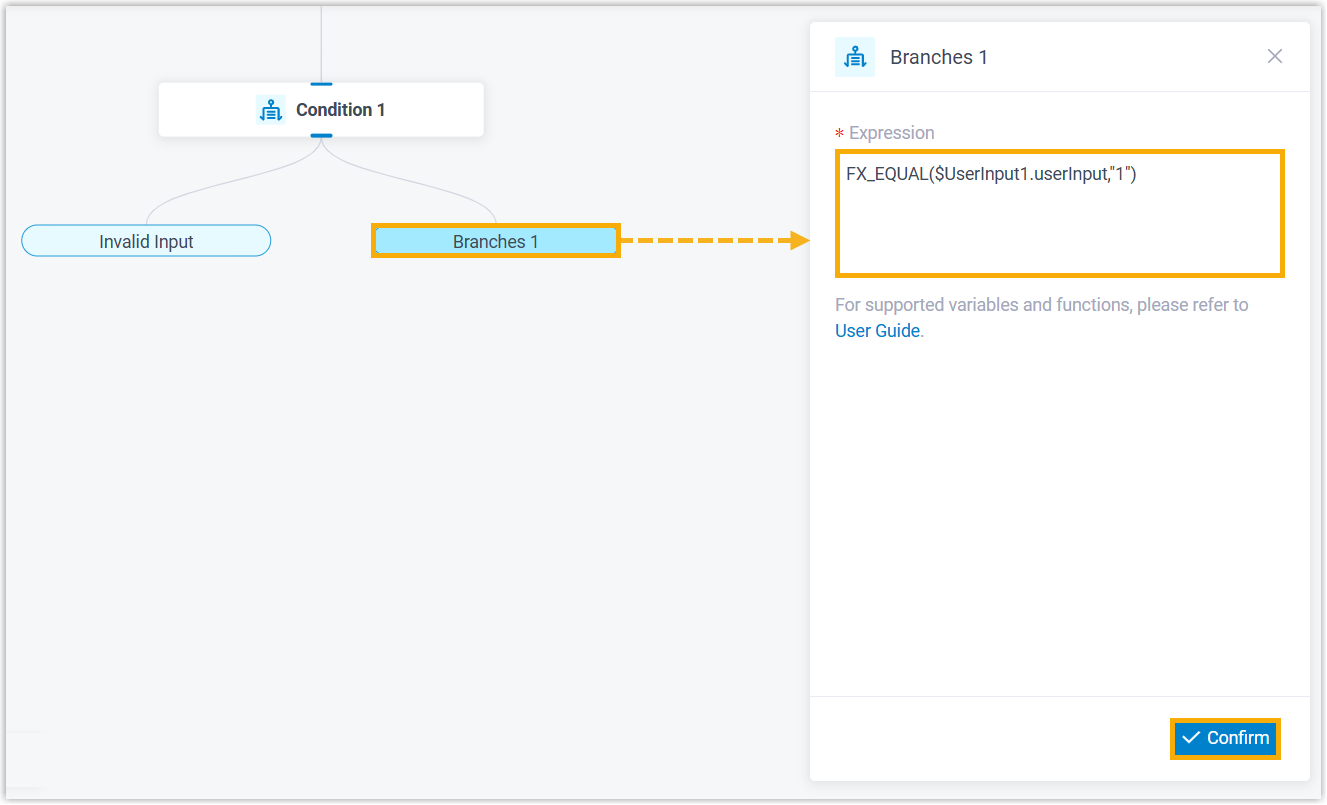
For example, enter FX_EQUAL($UserInput1.userInput,"1"). In this way, if the caller presses 1, the call will be routed to the component connected to the branch.
Note: For more information about the expression, see Variables and Functions in Yeastar Expression.
- Click
- Specify destination for no match
- Click
 on No Match to add a
component, which will be executed if none of the branch conditions are
met.
on No Match to add a
component, which will be executed if none of the branch conditions are
met.
Component connections
Condition component comes with a built-in No Match branch, and supports up to 10 additional branches for specific conditions.
Each branch can be connected on one component, which can be any of the components listed below.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Prompt |
Prompt component allows you to play audio prompt(s) or a text-to-speech message to callers. For more information, see Prompt. |
| Business Hours |
Business Hours component allows you to route calls to different destinations based on the time of day. For more information, see Business Hours. |
| Menu | Menu component allows you to present
callers with a set of menu options, and route calls based on the
DTMF digit they press. For more information, see Menu. |
| User Input |
User Input component allows you to collect DTMF digits from callers, typically used with Condition component to evaluate user input and route calls. For more information, see User Input. |
| Language |
Language component allows you to change the system prompt language for subsequent components in a call flow. For more information, see Language. |
| Record | Record component allows you to start
recording a call upon the caller being connected to another
participant, and optionally configure prompts to inform call
participants at the start and during the recording.
Alternatively, you can use the component to disable call
recording for calls that are supposed to be recorded. For more information, see Record. |
| Dial by Number |
Dial by Number component allows callers to directly dial a number to reach the destination. For more information, see Dial by Number. |
| Dial by Name |
Dial by Name component is one of the end components to terminate caller's connection to the current call flow. It allows callers to reach extension user by entering the first three letters of the user's name. For more information, see Dial by Name. |
| Transfer |
Transfer component is one of the end components to terminate caller's connection to the current call flow. It allows you to transfer callers to a designated destination, and optionally configure prompts to inform them of the transfer. For more information, see Transfer. |
| Hang Up Call |
Hang Up Call component is one of the end components to terminate caller's connection to the current call flow. When callers are routed to the component, the call will be disconnected. For more information, see Hang Up Call. |
| Condition | Condition component allows routing calls based on
logical expressions. For more information, see Condition. |
| Loop | Loop component allows a group of
components to be executed repeatedly, either for a specified
number of times or until a condition is met. For more information, see Loop. |
| Internal Data Ops | Internal Data Ops component allows you
to query and update data from PBX-native database. For more
information, see the following topics: |
| Email Sender | Email Sender component allows you to
send emails, enabling real-time notifications, alerts, or
delivery of user-specific information. For more information, see Email Sender. |
| Database Access | Database Access component allows you
to interact with database during a call flow. You can execute
SQL operations to retrieve or update data as needed. For more information, see Database Access. |
| HTTP Request | HTTP Request component allows you to
send HTTP requests to external web servers, enabling data
exchange with third-party services. For more information, see HTTP Request. |