Examples of Firewall Rules
In this topic, we provide configuration examples of firewall rules under different scenarios. We recommend that you configure firewall rules according to the network environment of your PBX.
- Add a trusted IP address to allowlist, or PBX may block the IP address as it frequently sends packets.
- Add an untrusted IP address to blocklist to prevent the IP address from accessing PBX.
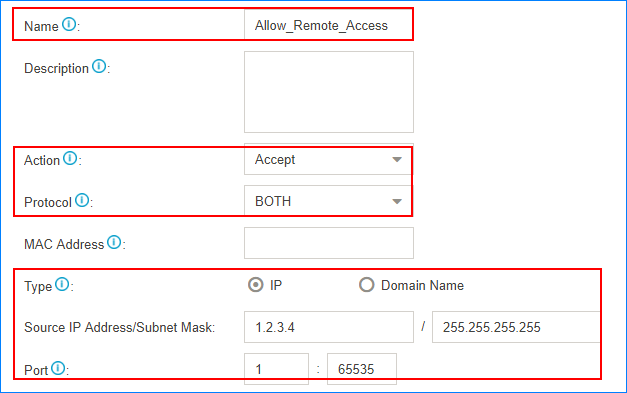
Accept remote extensions and remote web access
If you want to remotely access PBX web page or register extensions, you can add the public IP address to the allowlist, or PBX may block the public IP address as it frequently sends packets.
For example, the trusted public IP address is 1.2.3.4. Set the firewall rule as follows.
- The subnet mask 255.255.255.0 indicates that all IP addresses under the same network segment are allowed to access the PBX.
- If the remote place doesn't have a static public IP address, you can set a firewall rule for the trusted domain name.
Accept traffic of VoIP Provider
Accept the traffic of SIP registration port and RTP media ports from the VoIP provider.
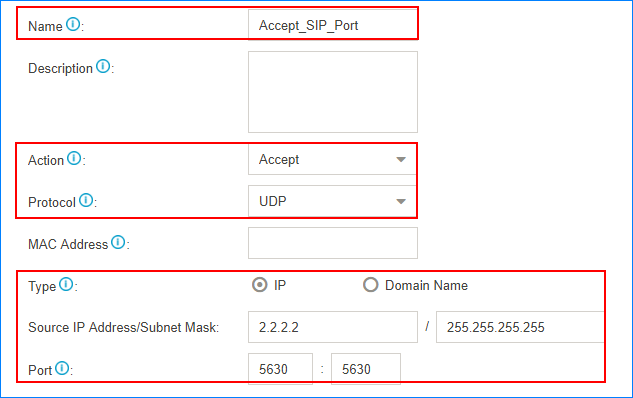
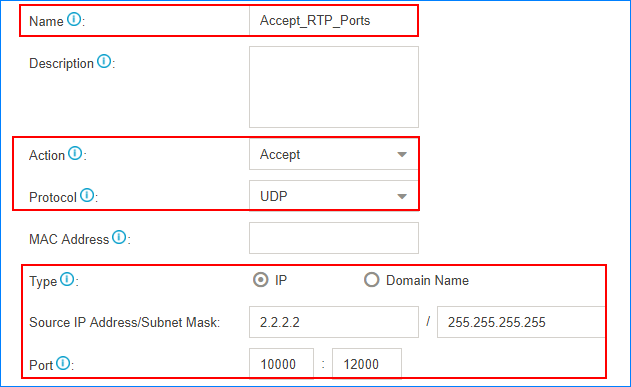
For example, the IP address of the VoIP provider is 2.2.2.2; port of SIP registration is 5630; the range of RTP ports is 10000-12000. You need to set two firewall rules for the VoIP provider.
- Accept traffic of the SIP registration port
- Accept traffic of the RTP ports
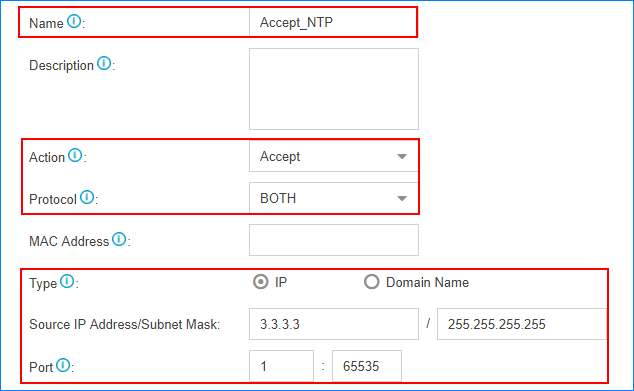
Accept traffic of NTP, SMTP, POP, STUN
We recommend that you accept traffic of NTP, SMTP, POP, STUN, and keep the default auto defense rules.
For example, the IP address of the NTP server is 3.3.3.3. Set the firewall rule as the following figure.